60th Anniversary Timeline
The Delaware River Basin Commission has been managing, protecting and improving our shared waters for 60 years and counting. As we celebrate this anniversary, we wanted to reflect on the Commission’s work and accomplishments throughout the Basin, set against the rich backdrop of historic actions, environmental milestones and major hydrologic events. Our work continues with opportunities and challenges ahead, and we invite you to join us in a shared journey through the next 60 years.
DRBC Milestone
Environmental Milestone
Hydrologic Milestone
Cultural or Historical Milestone
DRBC Milestone
Environmental Milestone
Hydrologic
Milestone
Cultural or Historical
Milestone
1967
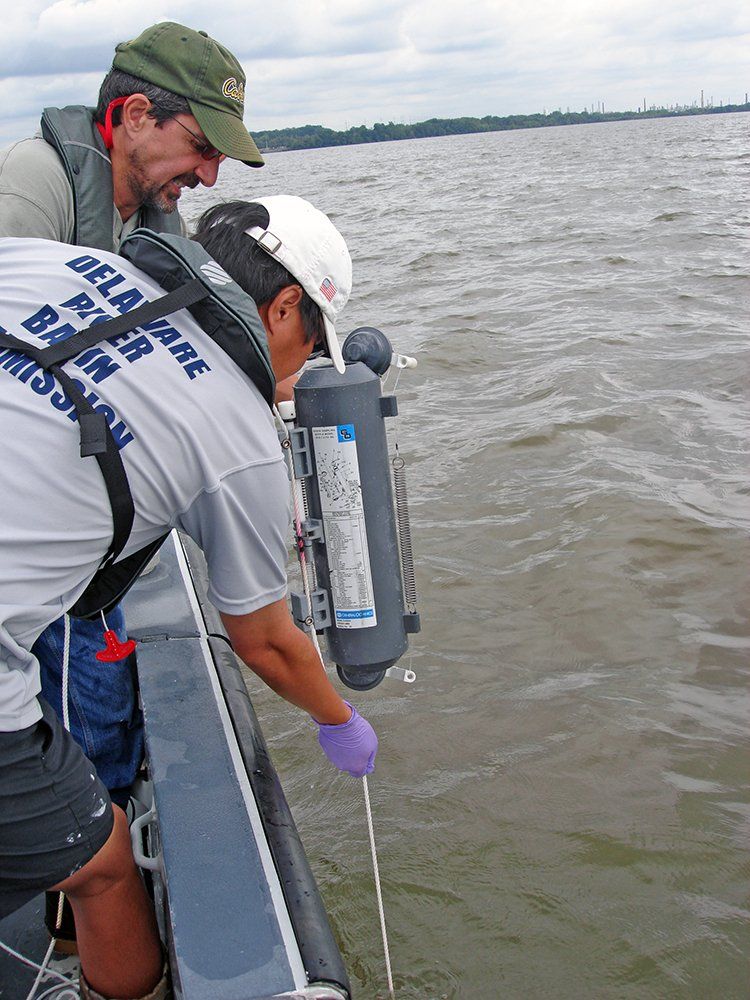
The Delaware Estuary Water Quality Monitoring Program (AKA the Boat Run) is established, a collaboration with the Delaware Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control. Today, this program is one of the longest, continuously running in the world.
City skyline
Credit: Del. Dept. Natural Resources & Environmental Control
City skyline
Credit: Del. Dept. Natural Resources & Environmental Control
1968
The DRBC adopts broad regulations to implement water quality standards for the Delaware Estuary that include an innovative wasteload allocation component. Former Interior Department head Stewart Udall remarks, "Only the Delaware among the nation’s river basins is moving into high gear in its program to combat water pollution."
City skyline
City skyline
1970
As part of a nationwide environmental movement, the first Earth Week was held April 16-22, with Earth Day officially observed on April 22. Over the next several years, departments of environmental protection and conservation are established by the federal government and each of the Basin states.
City skyline
Credit: Philadelphia Earth Week Committee; http://earthweek1970.org
City skyline
Credit: Philadelphia Earth Week Committee; http://earthweek1970.org
1971
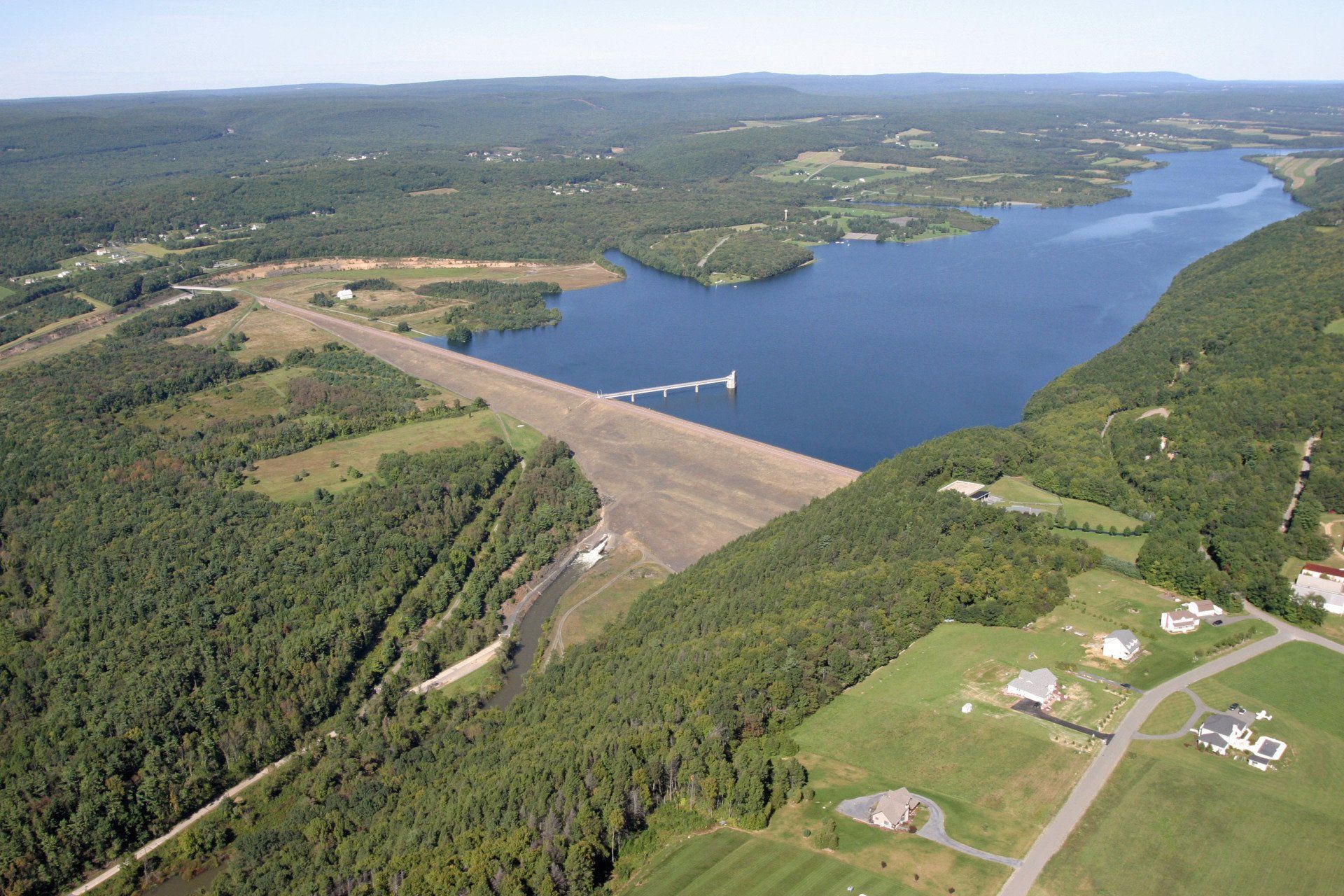
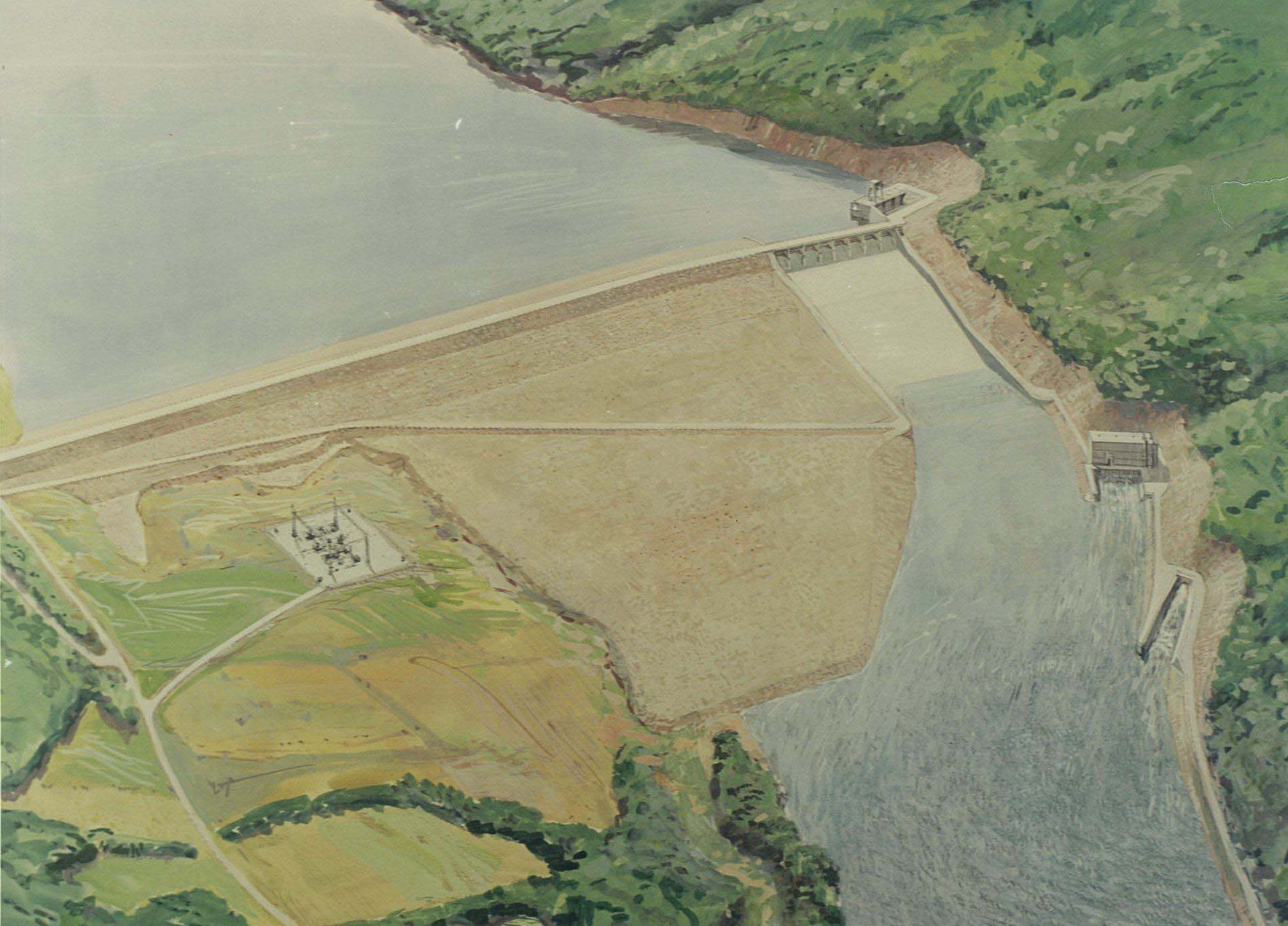
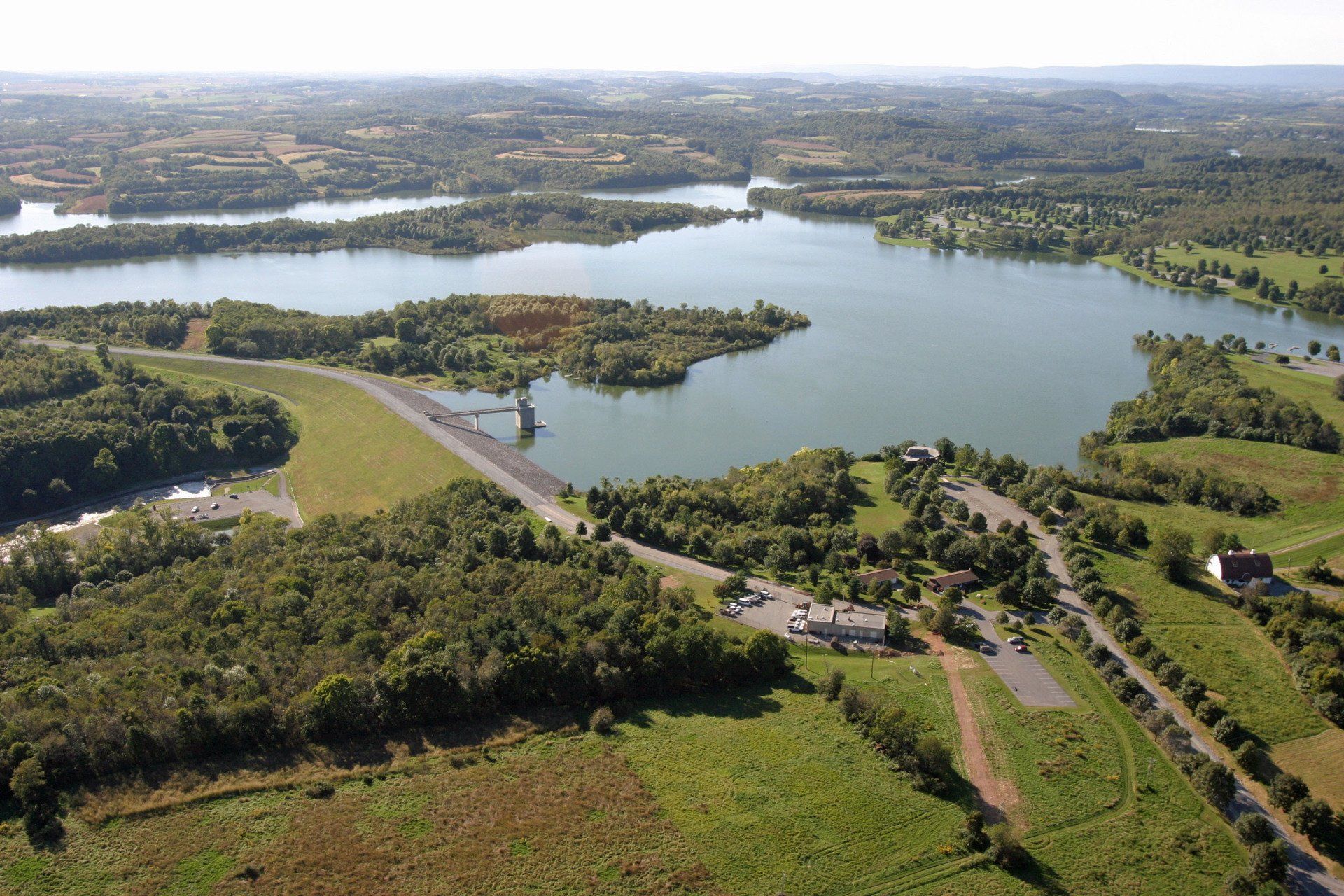
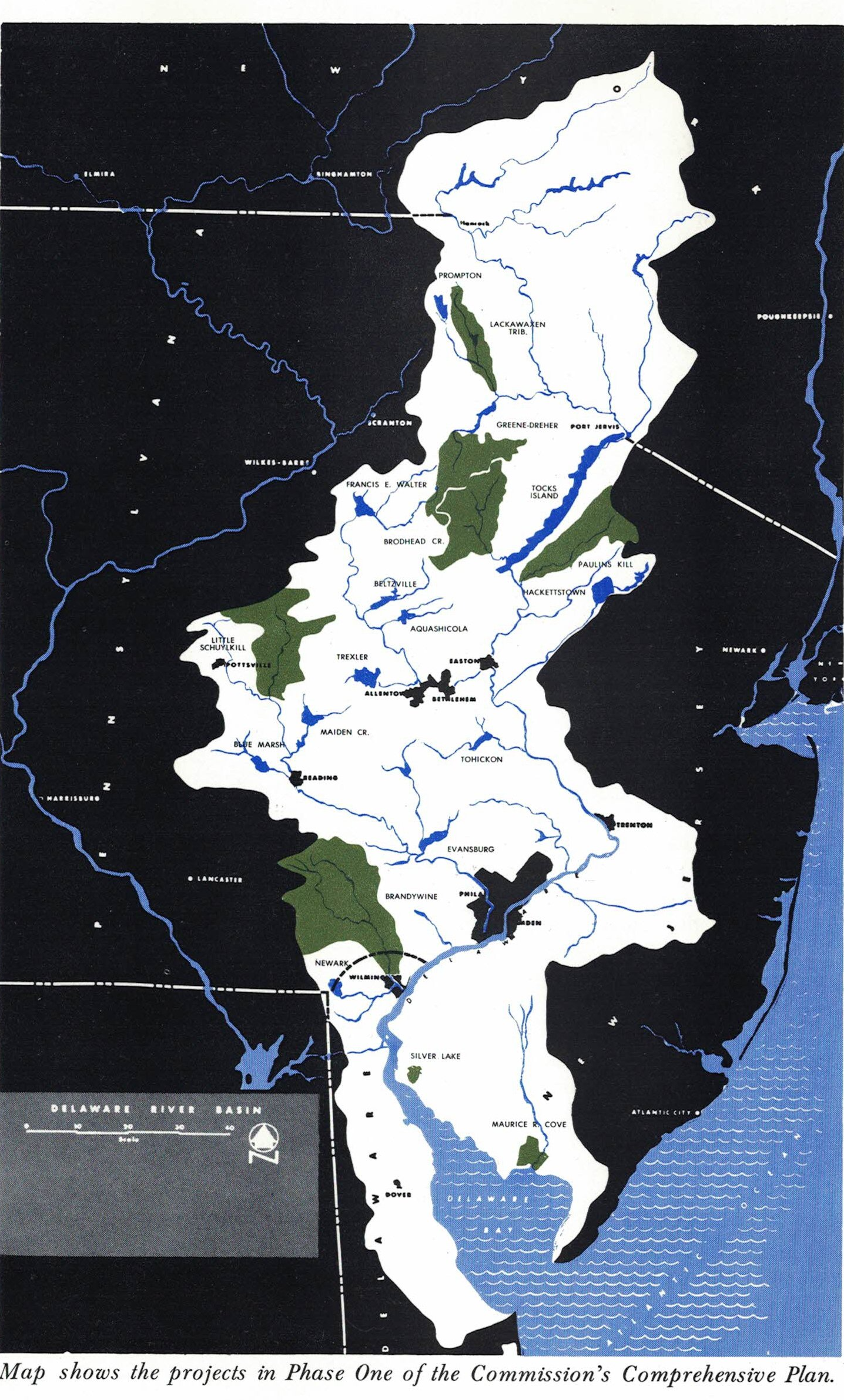
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers completes construction of the Beltzville Reservoir at the headwaters of the Lehigh River, with the DRBC as a local sponsor responsible for financing and directing use of a portion of the reservoir's storage capacity.
City skyline
Credit: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
City skyline
Credit: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
1972
Congress passes the Clean Water Act, consisting of extensive amendments to the Federal Water Pollution Control Act that include, among other things, a nationwide program for regulation by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency of pollutant discharges.
City skyline
City skyline
Photo credit here. If not, turn this off.
1979
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers completes construction of the Blue Marsh Reservoir on the Tulpehocken Creek, a tributary to the Schuylkill River, with the DRBC as a local sponsor responsible for financing and directing use of a portion of the reservoir's capacity. The multi-purpose dam supports flood control, water supply, water quality, and recreation.
City skyline
Credit: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
City skyline
Credit: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
1980
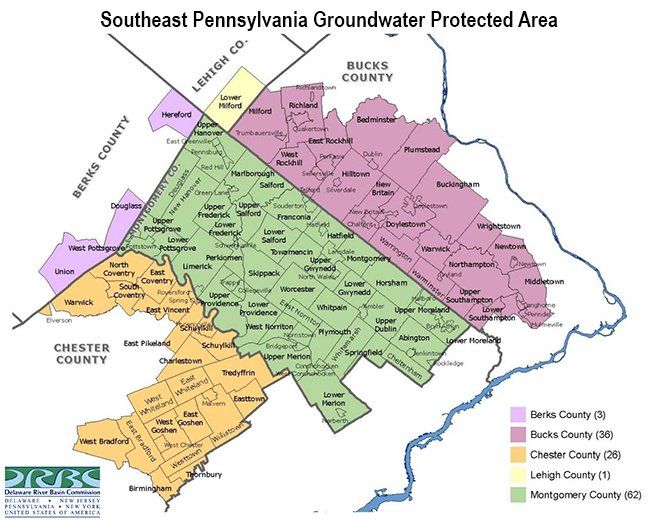
At Pennsylvania's request, DRBC establishes the Southeastern Pennsylvania Groundwater Protected Area to address over-pumping of groundwater as a result of rapid development in this region. The program limits groundwater withdrawals and encourages conjunctive use of surface and groundwater sources.
City skyline
City skyline
1983
Through coordination by the DRBC, the parties to the Supreme Court litigation over allocation of the Basin's waters reach the historic Good Faith Agreement. The Agreement establishes recommendations that include reductions in flow targets, diversions and releases to conserve water during periods of low flow and drought, and identify additional storage projects to meet projected future demand in the absence of a main stem dam.
City skyline
City skyline
1987
The Clean Water Act Amendments of 1987 establish the National Estuary Program to develop and implement conservation and management plans for protecting estuaries and restoring and maintaining their chemical, physical, and biological integrity, as well as controlling point and nonpoint pollution sources. Under new Section 320 of the CWA, states may nominate or the EPA may identify estuaries of national significance and convene a management conference for that estuary.
City skyline
Credit: Restore America's Estuaries
City skyline
Credit: Restore America's Estuaries
1989
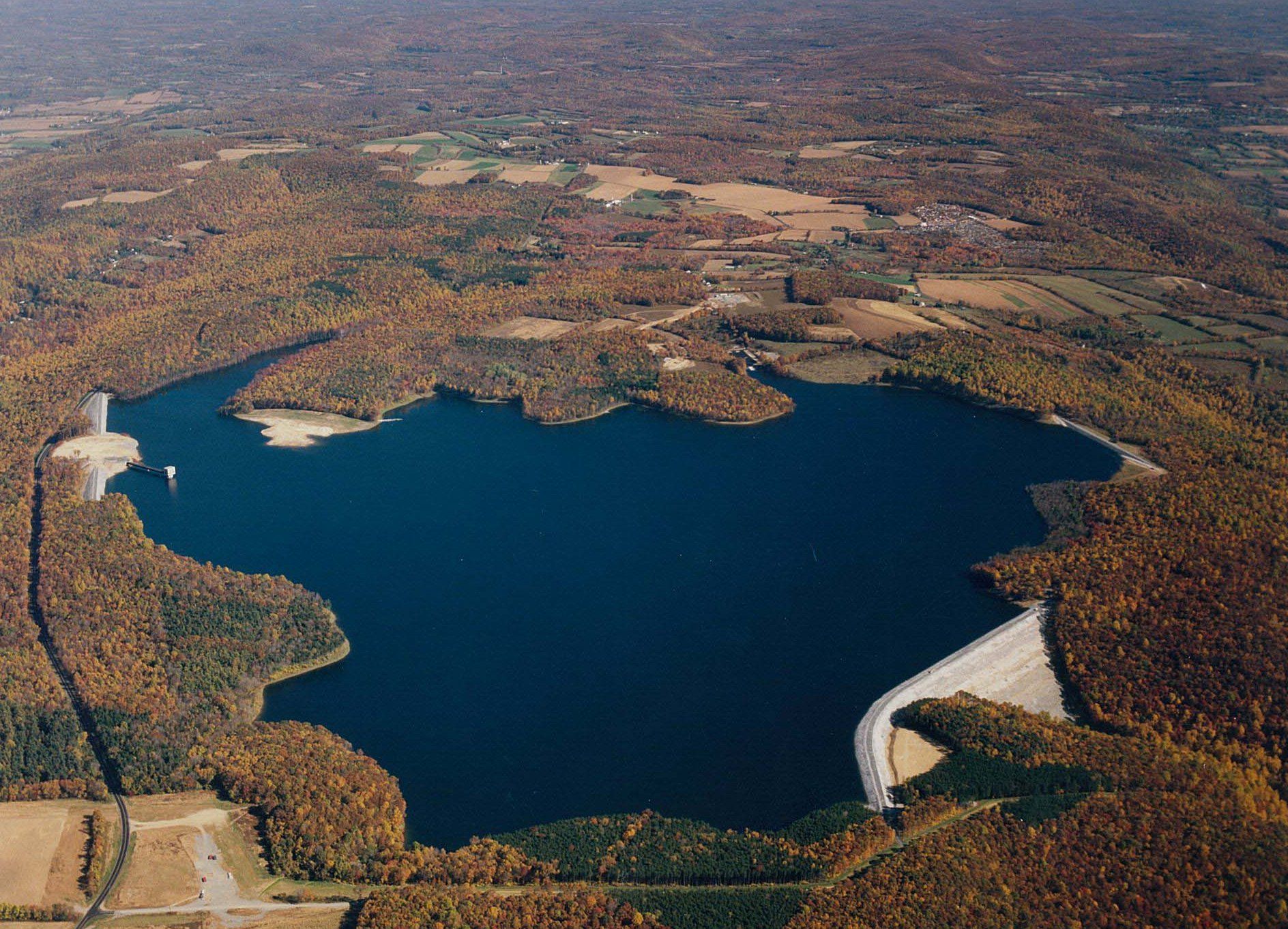
After DRBC identifies the need for additional storage to ensure access to cooling water and preserve minimum streamflows during drought, a group of power generators completes construction of Merrill Creek Reservoir. During drought conditions in the lower Delaware Basin, the project provides water for electric generating utilities, helping them avoid cutbacks.
City skyline
City skyline
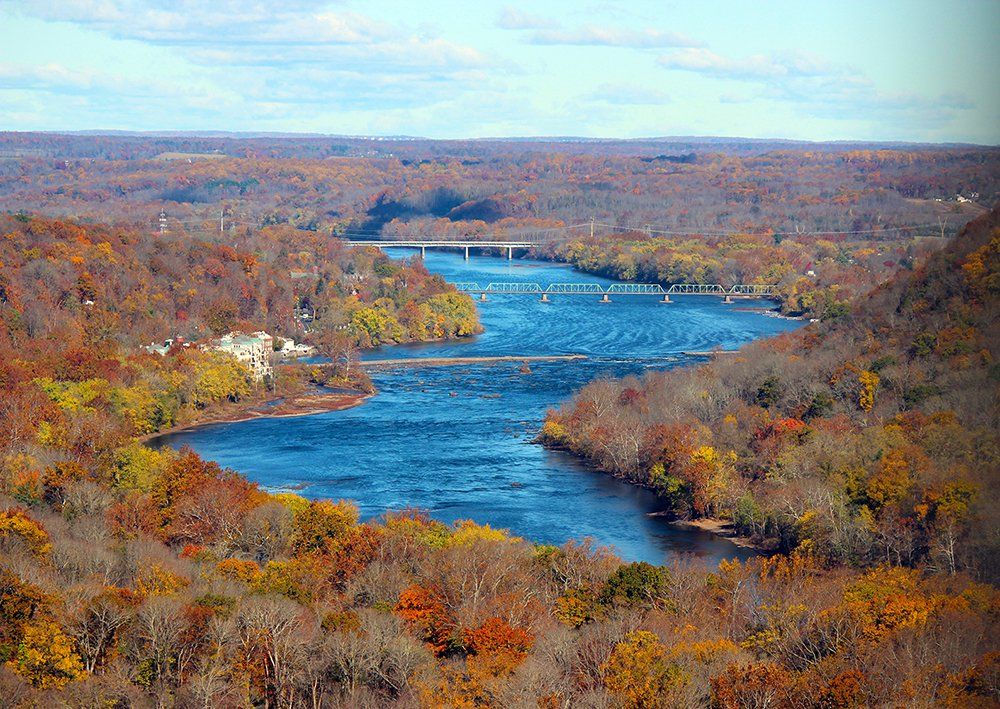
2000
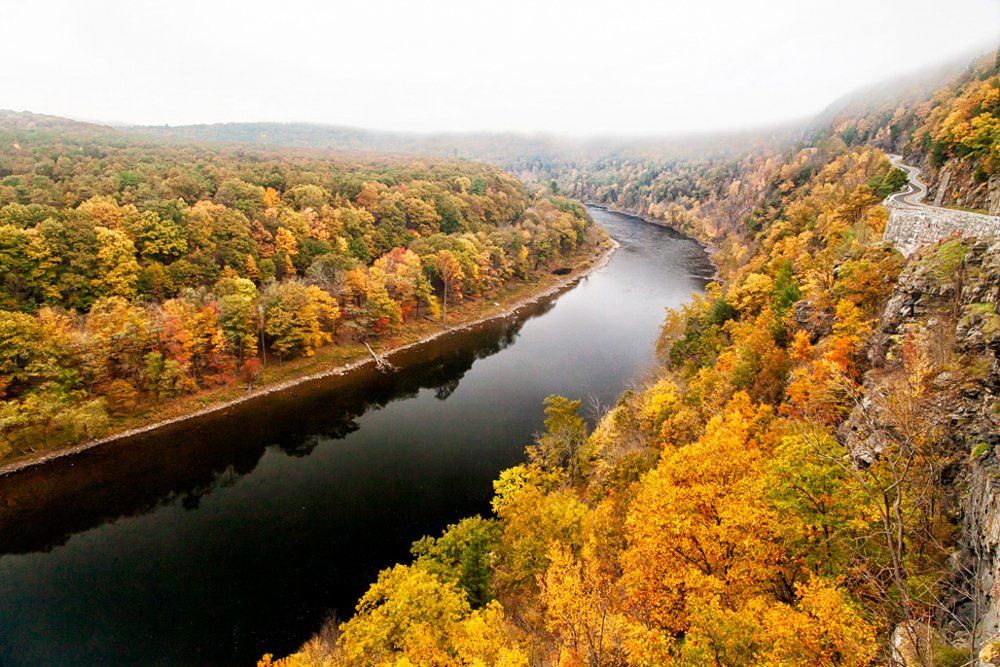
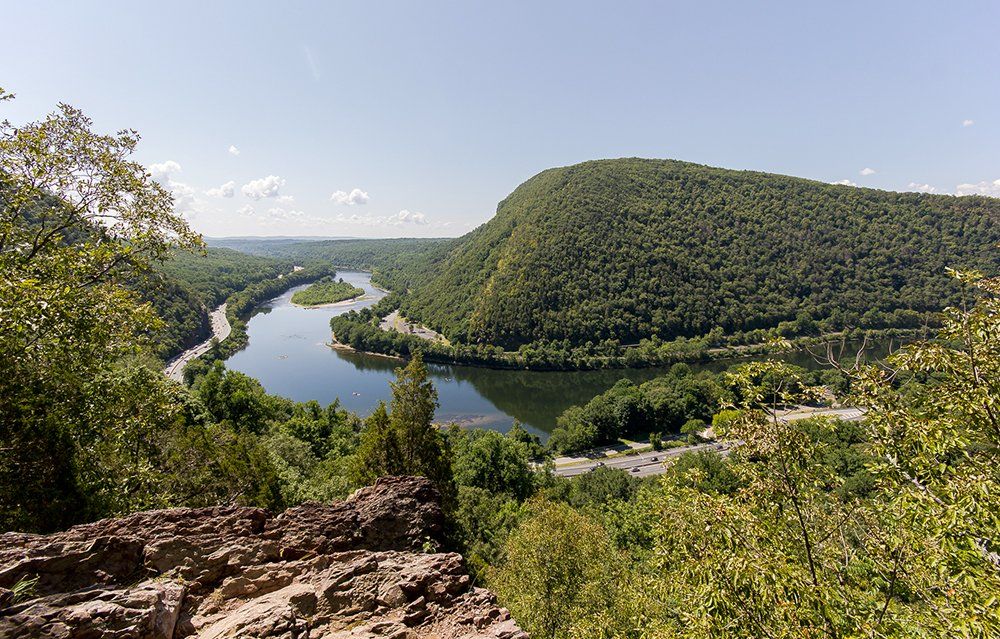
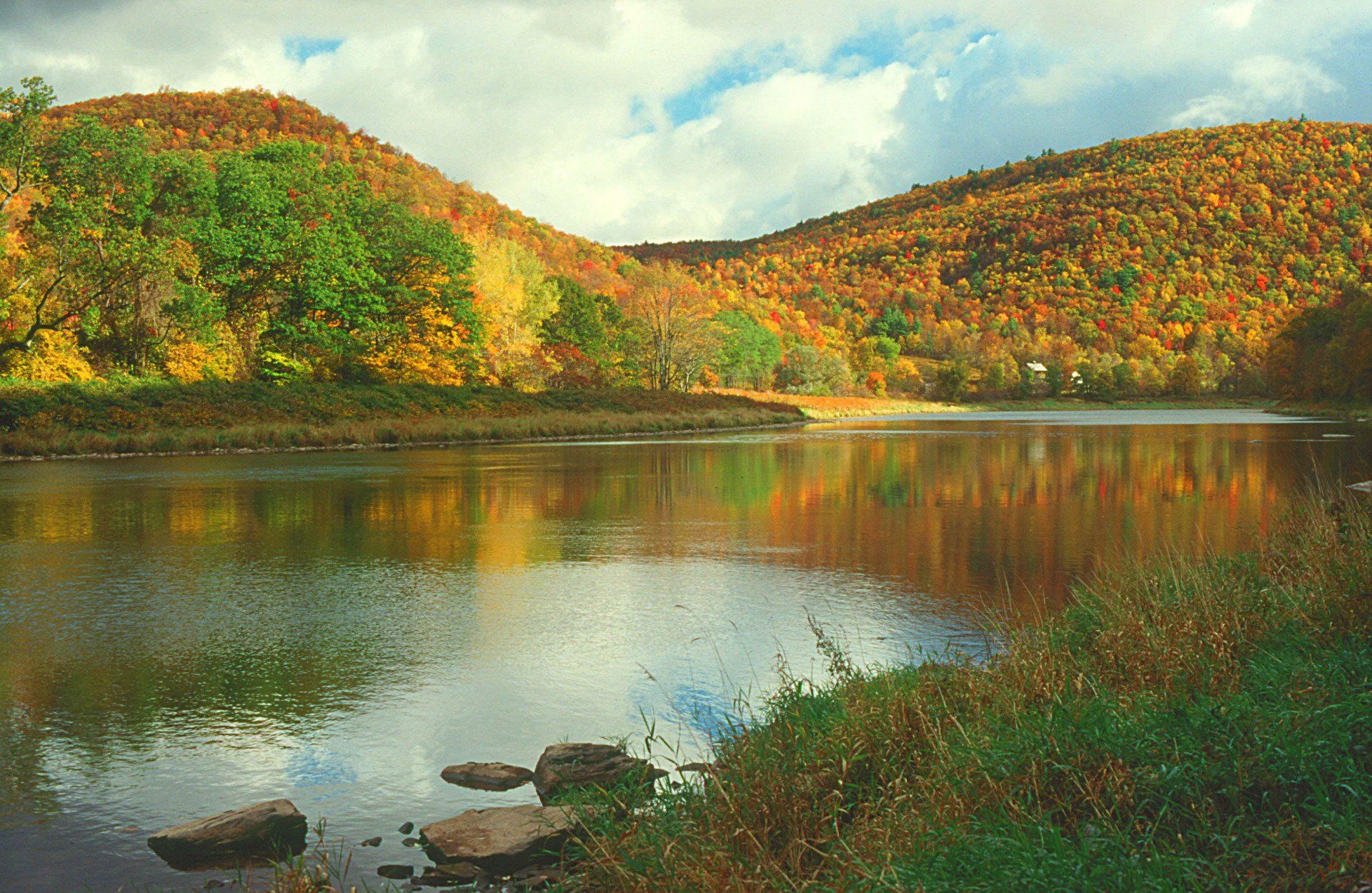
The non-tidal section of the main stem known as the Lower Delaware is added to the National Wild and Scenic Rivers System. Wild and Scenic Rivers protection now covers 75% of the non-tidal Delaware River. Tributaries already in the System include White Clay Creek and Maurice River; the Musconetcong River is added in 2006.
City skyline
Credit: Keith Balderston
City skyline
Credit: Keith Balderston
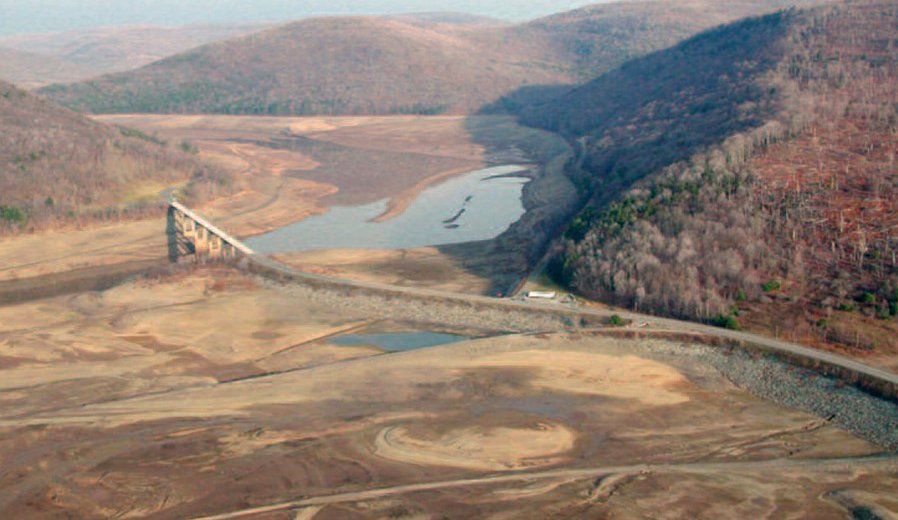
2001
The DRBC declares a basinwide drought emergency for the third time since 1980, and combined storage in the three New York City Delaware reservoirs drops to a record-low level. This emergency will remain in effect through 2002.
City skyline
Credit: NYC Dept. of Environmental Protection
City skyline
Credit: NYC Dept. of Environmental Protection
2002
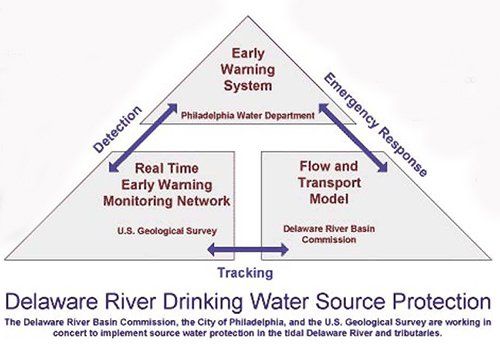
Philadelphia Water Department partners with DRBC, Pennsylvania DEP and others to launch an Early Warning System—a monitoring, communication and notification system for potential water quality events—to water suppliers and industrial intake operators in the Schuylkill and Delaware River watersheds.
City skyline
City skyline
Photo credit here. If not, turn this off.
2006
On behalf of Delaware and New Jersey, and based on work conducted by the DRBC, U.S. EPA establishes a TMDL for PCBs in the Delaware Bay. This TMDL was built upon the TMDLs developed in 2003 for the 85-mile tidal section of the Delaware River.
City skyline
City skyline
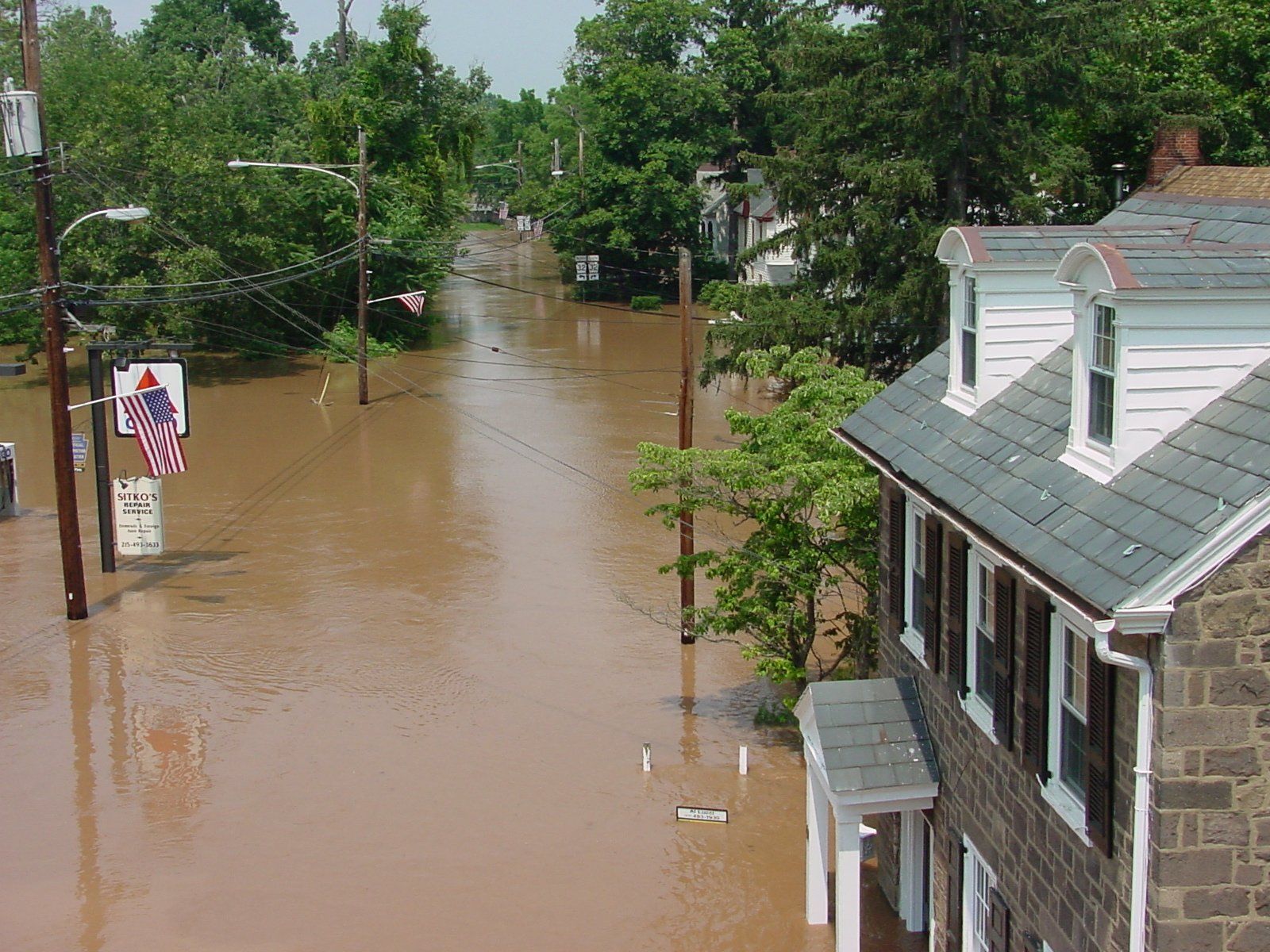
2007
The Interstate Flood Mitigation Task Force, convened at the request of Basin-state governors after three devastating mainstem floods in 2004, 2005 and 2006, completes work and recommends a more proactive, sustainable, and systematic approach to flood damage reduction.
City skyline
City skyline
2008
The DRBC permanently designates 76 miles of the Lower Delaware as Significant Resource Waters under DRBC's Special Protection Waters program, a major step toward "keeping the clean water clean." The antidegradation regulations now include the entire non-tidal Delaware River.
City skyline
Credit: Linda Park
City skyline
Credit: Linda Park
2009
In response to 150 million gallons per day of water lost in the Basin, DRBC institutes an innovative water efficiency program to identify and control water loss. This new "water audit" approach will improve water supply efficiency and enhance the Commission's water conservation program.
City skyline
City skyline
2011
The Delaware River is designated Pennsylvania's "River of the Year" by the Department of Conservation and Natural Resources. The Commonwealth also honored the Delaware as River of the Year in 2002.
City skyline
City skyline
Photo credit here. If not, turn this off.
2018
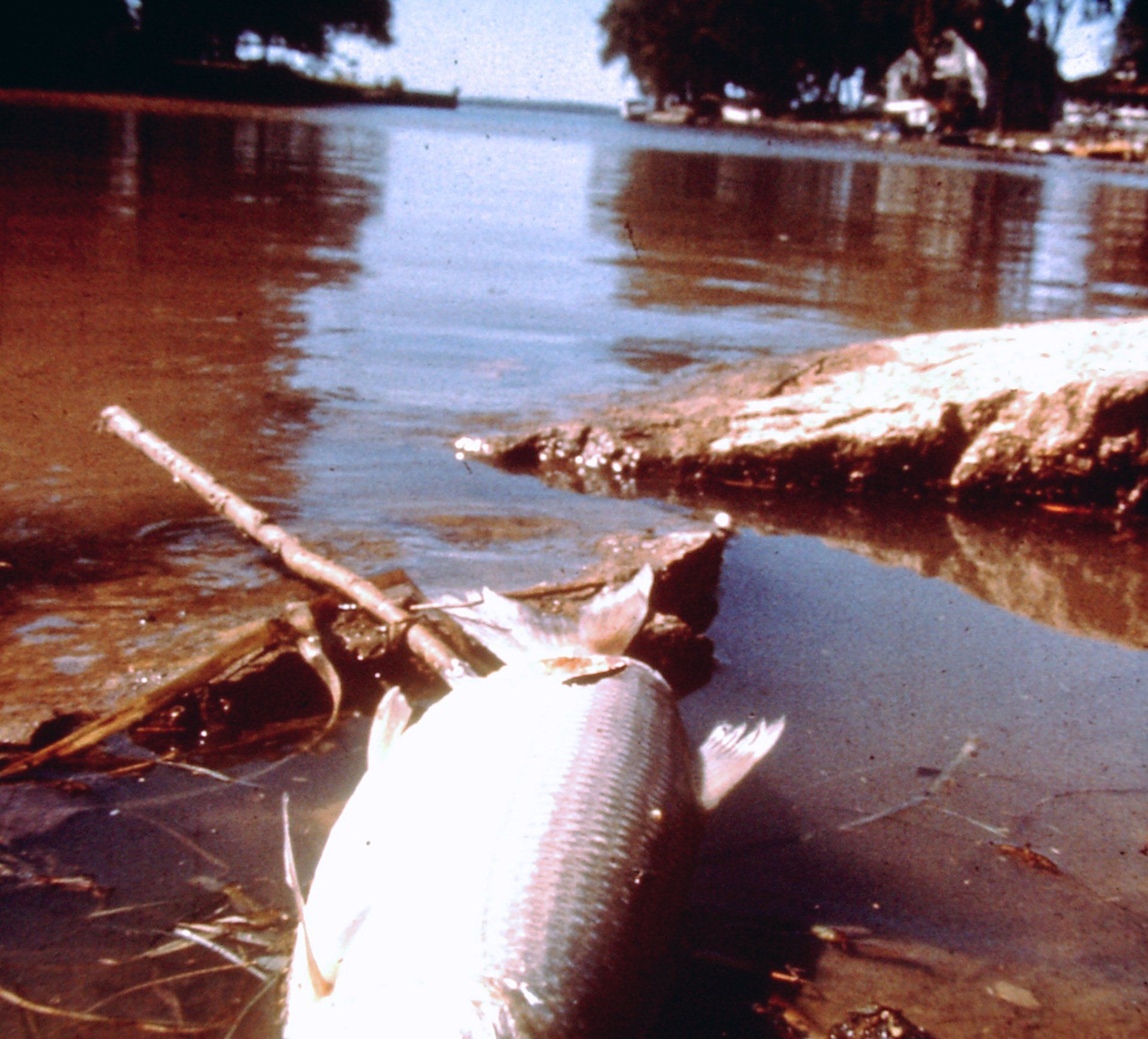
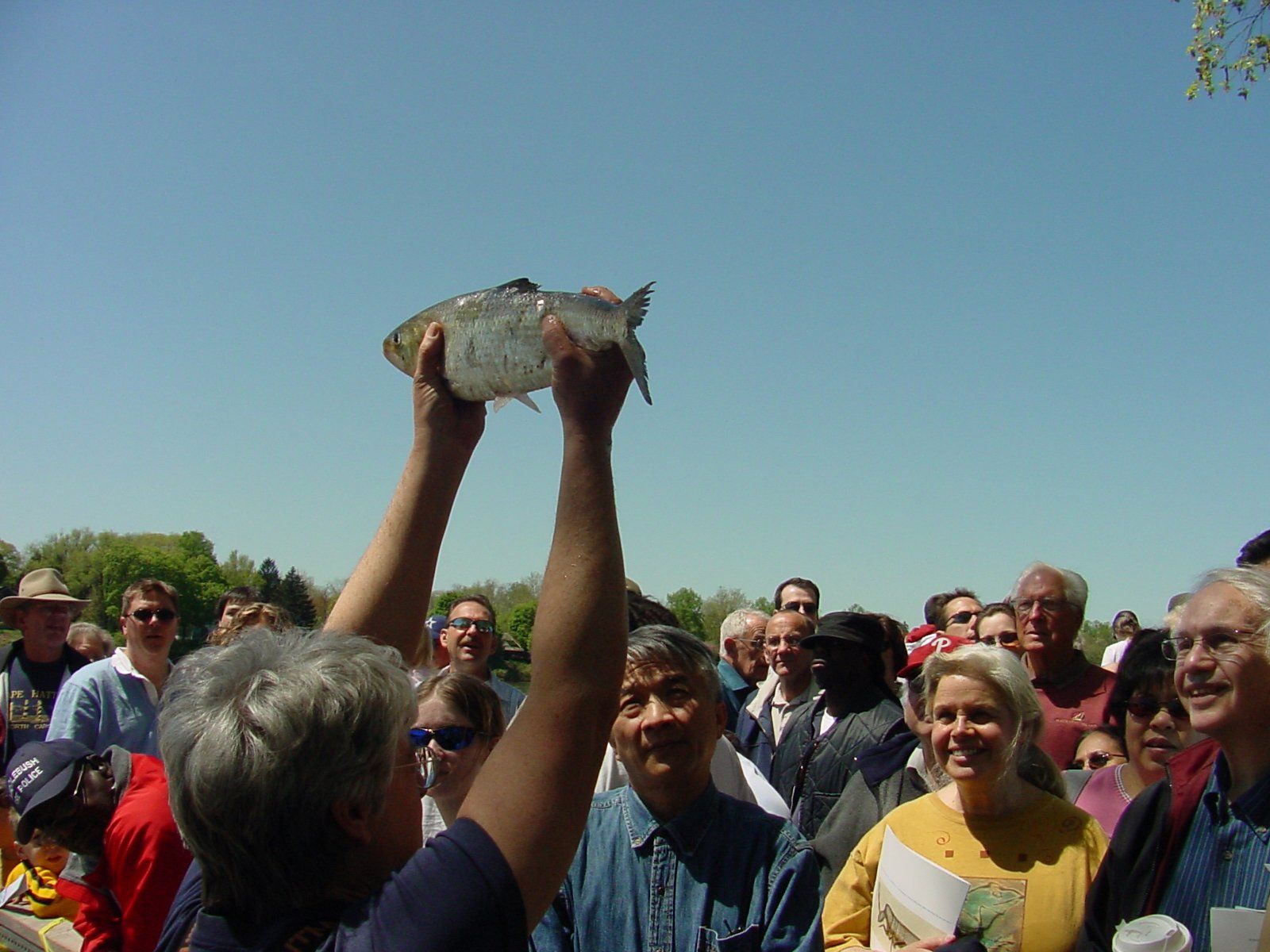
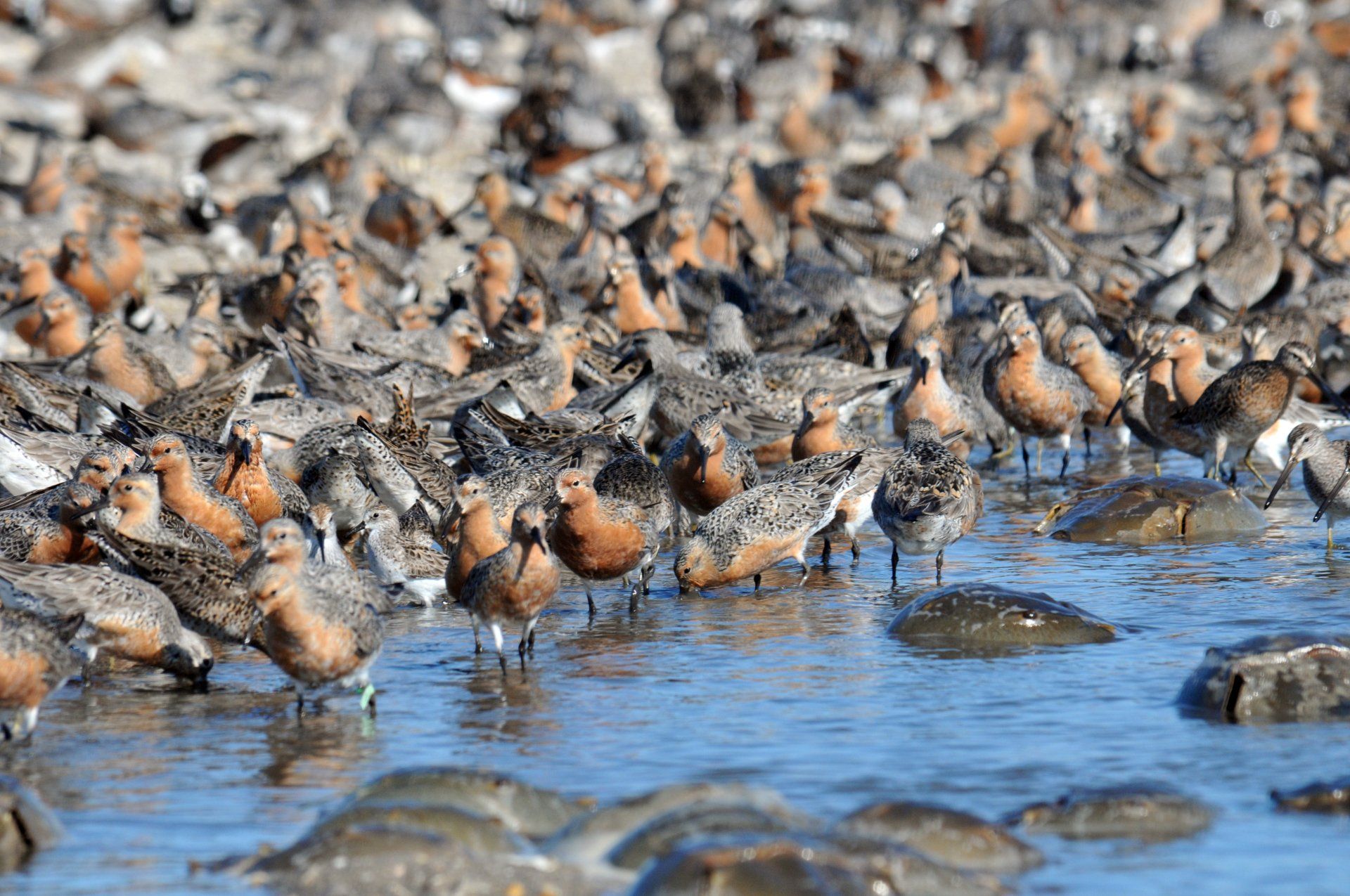
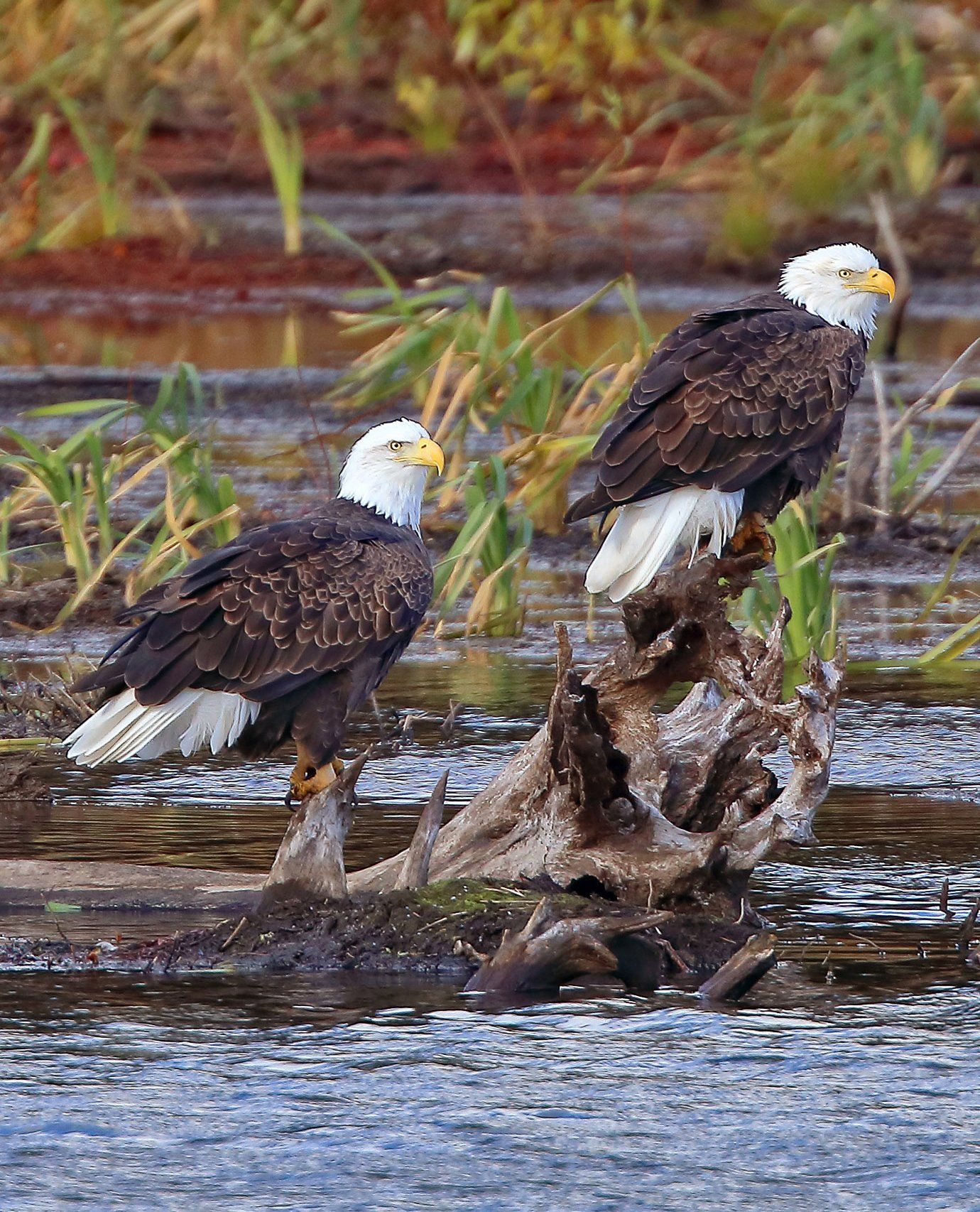
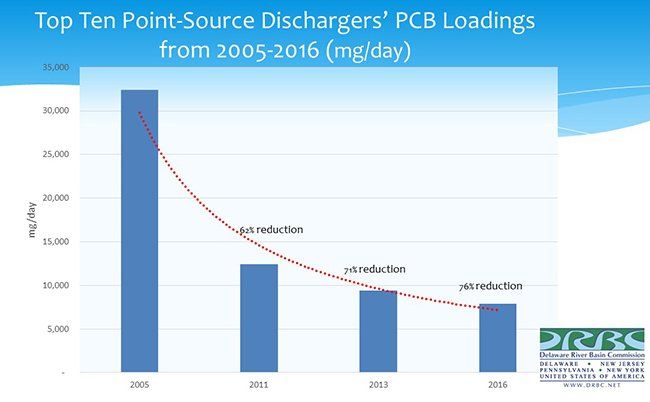
The states of Delaware and New Jersey relax fish consumption advisories for their shared waters of the Delaware Estuary and Delaware Bay as a result of improvements in PCBs and other legacy pollutants, through the cooperative efforts of DRBC and state environmental agencies.
City skyline
City skyline
2019
The DRBC issues its latest State of the Basin Report and launches Our Shared Waters. Together, these programs increase transparency into current conditions, provide a platform to measure progress, and enable DRBC to connect to communities.
City skyline
City skyline
2021
The DRBC votes to prohibit high volume hydraulic fracturing within the Delaware River Basin. The Commissioners also agree to propose rules for importing and exporting basin waters in connection with the practice.
City skyline
Credit: David B. Soete
City skyline
Credit: David B. Soete